Energy Savings Performance Contracting
The Performance Contracting National Resource Center (PCNRC) Training Certificate Series is an accredited, on-demand interactive eight-part series designed to support performance contracting and workforce development in the federal and MUSH markets (i.e., municipalities and state governments, universities and colleges, K-12 schools, and hospitals), provided at no cost to trainees. This training series supports the professional development of emerging and experienced professionals alike and provides the opportunity for individuals to earn continuing education credits and demonstrate their proficiency in performance contracting. See this one-pager from the U.S. Department of Energy for more information.
Description: Briefing document that introduces ESPCs as a mechanism for project implementation, and describes how ESPCs can deliver value for schools in terms of delivering energy savings and reducing operating costs, while improving occupant comfort and productivity.
Factsheet that summarizes ESPC performance metrics based on projects entered in the NAESCO database, namely implementation cost, energy performance and energy cost savings and simple payback period.
Description: Briefing document that outlines the value of including an Owner’s Representative on the customers project team. The value of this approach is typically well understood by practitioners, given the range of issues involved in moving a project through the development process, all the while ensuring good practices are maintained, and preserving value for the customer.
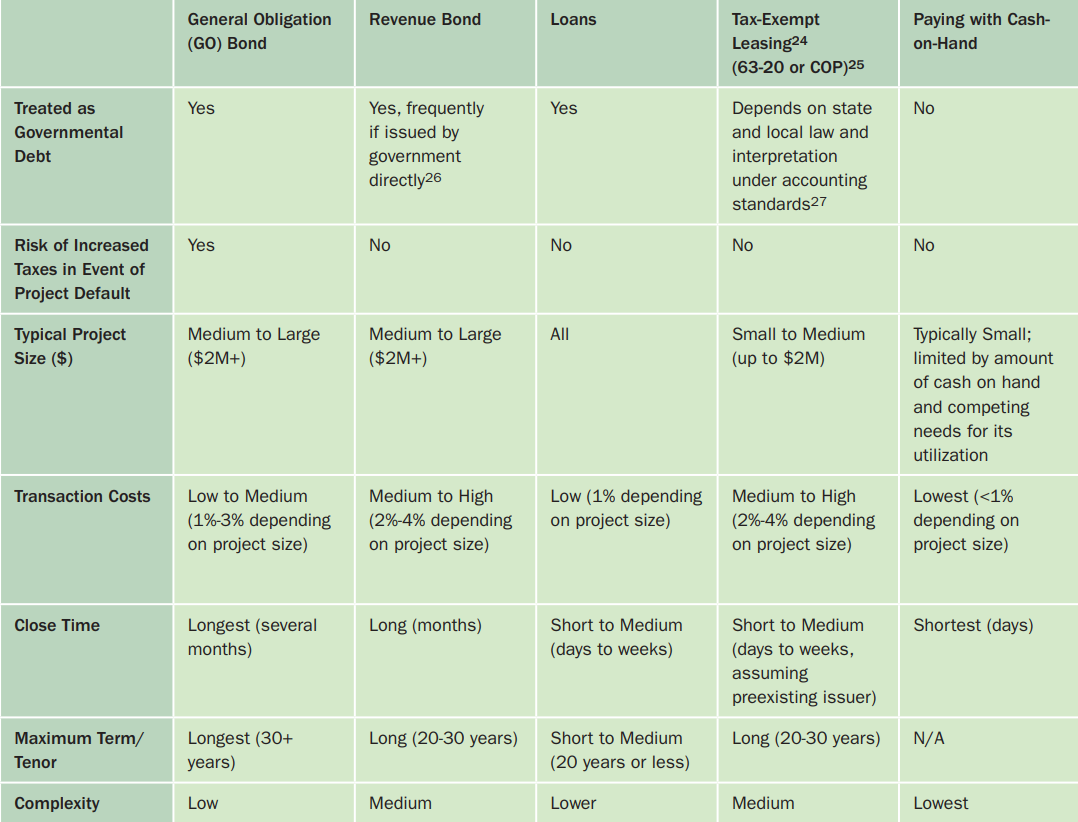
Comprehensive, high-level review of project financing options specific to the K-12 sector, including a summary of standard public and private sector offerings. Case studies including in the document provide additional detail on each of the options identified.
Paper describing how energy services performance contracts (ESPCs), tax-exempt lease-purchase agreements, energy efficiency bonds, and state green banks may offer you practical solutions when no money is available in the current budget for further improvements. It also provides clear financial reasoning and cost modeling, which demonstrate that energy efficiency projects really can pay for themselves within existing operating and capital budgets.
October 2020:
Guide for non-finance experts, describing how bonds may be accessed and utilized to pay for energy efficiency and renewable energy projects.
Guide describing financing mechanisms available to municipal and State entities such as public schools. Along with an overview of these, it outlines the roles that State and local government offices can adopt to support successful implementation.
Briefing document providing state ESPC program administrators—the individuals who oversee or provide ESPC technical support to their constituent state, local, healthcare, and/or educational facilities—with a selection of tested strategies to support successful M&V of ESPCs implemented in the state and local public sector.
eProject eXpress (ePX) provides a streamlined, tailored pathway for state and local governments to document, track, and demonstrate the ongoing value of their energy savings performance contracting (ESPC) projects and programs.
Leveraging the established eProject Builder (ePB) platform—a robust online energy project data management system—ePX unlocks new capabilities to meet the unique data management and reporting needs of the municipal and state governments, universities and colleges, schools, and hospitals (MUSH) market.
ePX is sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and hosted by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL).
Website page formatted interactive guide to support the complete and best practice implementation of ESPC projects. In general, it aims to support state and local practitioners considering ESPCs as a project implementation vehicle, better understand the process and necessary steps through to project execution. In particular, it is intended as a handholding resource for potential new customer stakeholders.
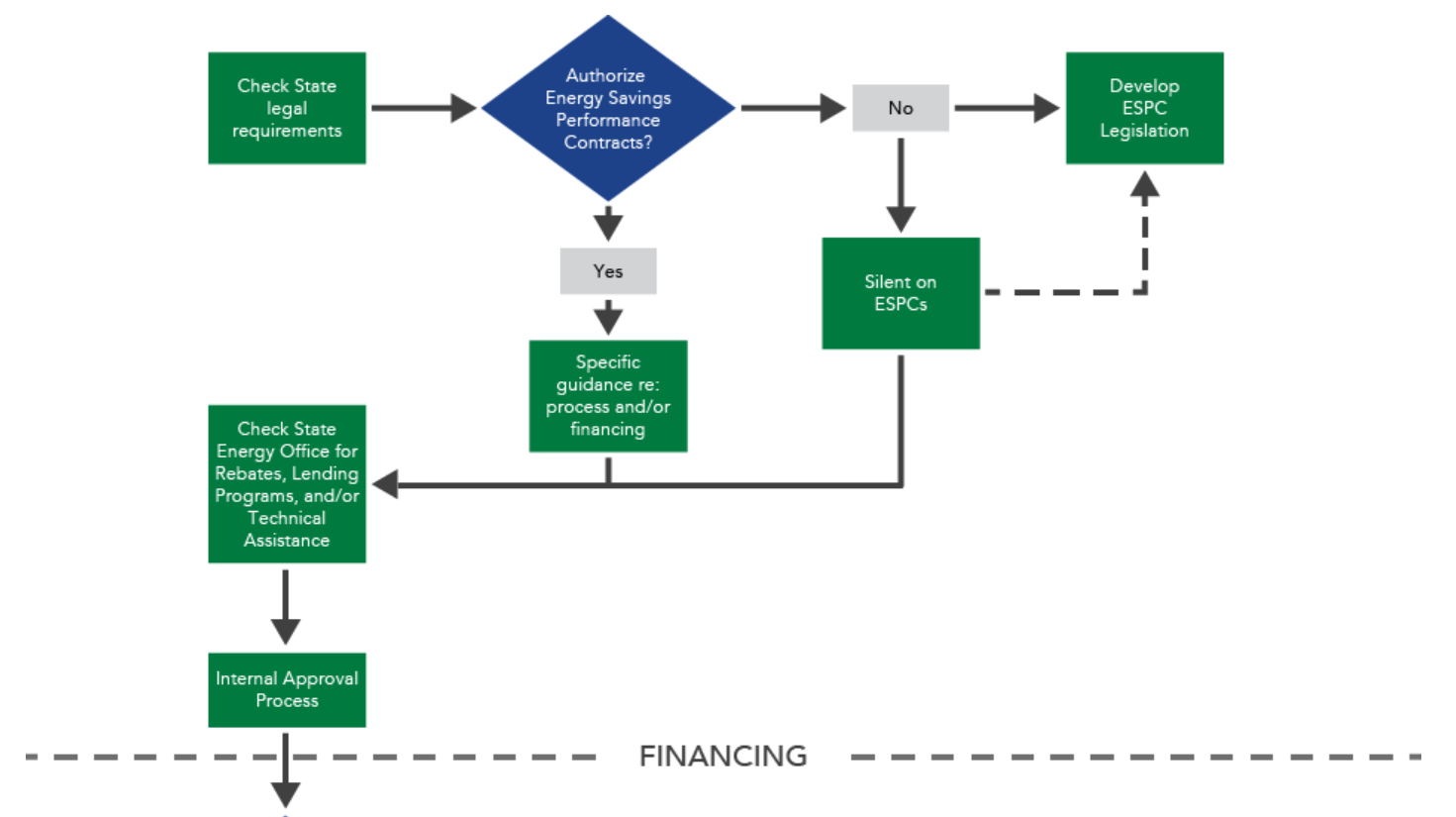
Flowchart that walks users through the potential financing options available for State and City government ESPC projects – the assumption is that this will be broadly applicable to school districts, although this requires confirmation.
One pager containing a list of questions around the characteristics of potential projects that supports preliminary self-diagnosis to determine whether ESPC is an appropriate delivery vehicle for specific projects, and also quick filter for project prioritization.
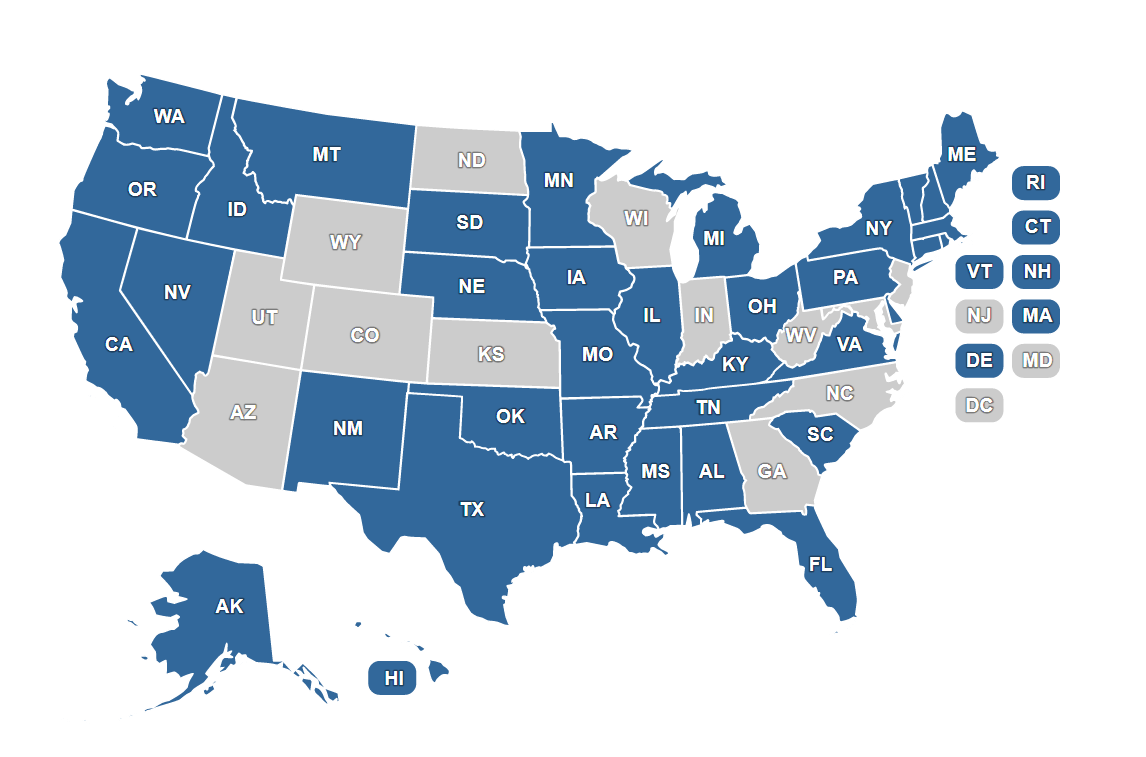
Online interactive guide to State-approved energy project financing programs across the US by individual State, including Green Bank, PACE, and on-bill financing.
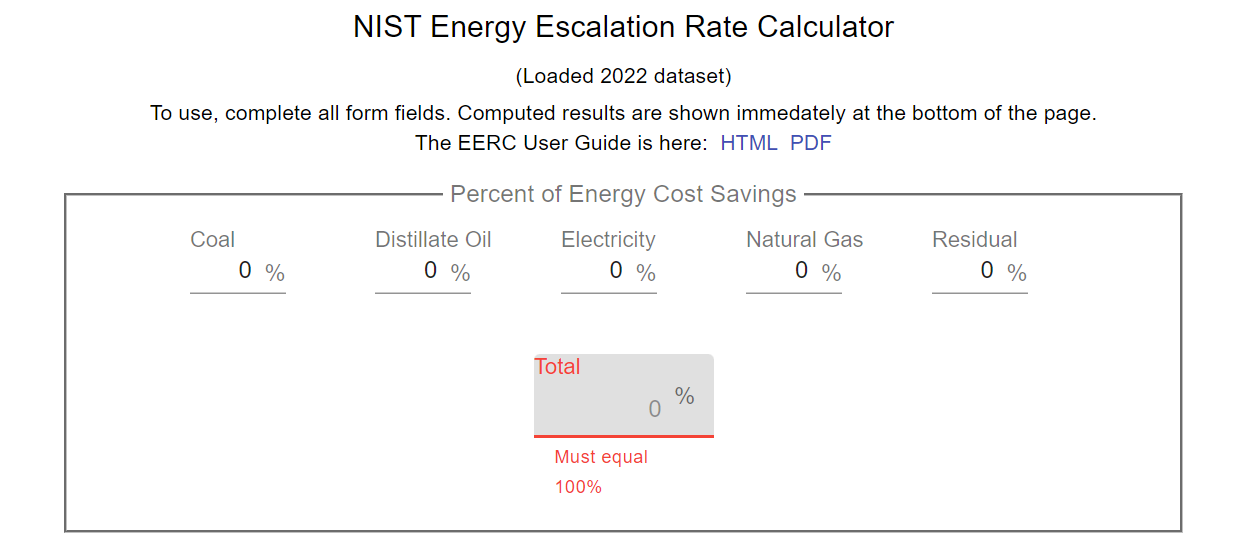
Tool for estimating escalation rates for ESPC project payments year-on-year and over the term of the contract. This tool appears designed for use at the contracting stage, in order to compare ESCO terms offered with an independent, calculated benchmark.
YouTube-hosted webinar of the same material included in the Virtual Technical Assistant. In this format, subject matter experts present the material, describing the challenges and key considerations of implementing projects at each step, and field questions from participants on the original webinar. There are 5 webinars in total, with between 40 mins and around one hour of content in each one.
Topics: considering ESPC, implementing ESPC projects, establishing an EPSC program, expanding ESPC to new markets, evaluating ESPC results
Exhaustive list of model documents for ESPC contracting process. Reference to these documents will help avoid significant early work in the following major areas:
- Prequalifying and selecting potential ESCO partners
- Executing an investment grade audit with an ESCO partner
- Implementing an Energy Savings Performance Contract
- Negotiating financing terms and associated energy performance
These are a model document only and do not attempt to identify or address all circumstances or conditions.